astronomer: A scientist who works in the field of research that deals with celestial objects, space and the physical universe.
atmosphere: The envelope of gases surrounding Earth or another celestial body.
corona: The envelope of the sun (and other stars). The sun’s corona is normally visible only during a total solar eclipse, when it is seen as an irregularly shaped, pearly glow surrounding the darkened disk of the moon.
diameter: The length of a straight line that runs through the center of a circle or spherical object, starting at the edge on one side and ending at the edge on the far side.
engineer: A person who uses science to solve problems. As a verb, to engineer means to design a device, material or process that will solve some problem or unmet need.
eruption: (in geoscience) The sudden bursting or spraying of hot material out through the surface of some planet, moon or star. Volcanic eruptions on Earth usually send hot lava, hot gases or ash into the air and across surrounding land. In colder parts of the solar system, eruptions often involve liquid water spraying out through cracks in an icy crust. This happens on Enceladus, a moon of Saturn that is covered in ice.
field: (in physics) A region in space where certain physical effects operate, such as magnetism (created by a magnetic field), gravity (by a gravitational field), mass (by a Higgs field) or electricity (by an electrical field).
Hawaii: This central Pacific island chain became the 50th U.S. state on Aug. 21, 1959. Moving from west to east, its eight major islands are Niihau, Kauai, Oahu, Molokai, Lanai, Kahoolawe, Maui, and Hawaii (also known as the Big Island). The entire crescent-shaped island chain spans some 2,400 kilometers (1,500 miles). Each of the state’s islands was created from one or more volcanoes that long ago sprang up from the ocean floor. The chain sits some 3,857 kilometers (2,397 miles) west of San Francisco, Calif., and 8,516 kilometers east of Manila, the Philippines.
insight: The ability to gain an accurate and deep understanding of a situation just by thinking about it, instead of working out a solution through experimentation.
magnetic field: An area of influence created by certain materials, called magnets, or by the movement of electric charges.
NASA: Short for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Created in 1958, this U.S. agency has become a leader in space research and in stimulating public interest in space exploration. It was through NASA that the United States sent people into orbit and ultimately to the moon. It also has sent research craft to study planets and other celestial objects in our solar system.
National Science Foundation: The U.S. Congress created this independent federal agency in 1950 to promote the advancement of science; national health, prosperity and welfare; and the nation’s defense. This agency funds nearly one-fourth of all federally supported basic research in U.S. colleges and universities. In many fields such as mathematics, computer science and the social sciences, NSF is the major source of federal funding.
observatory: (in astronomy) The building or structure (such as a satellite) that houses one or more telescopes.
orbiter: A spacecraft designed to go into orbit, especially one not intended to land.
plasma: (in chemistry and physics) A gaseous state of matter in which electrons separate from the atom. A plasma includes both positively and negatively charged particles.
poles: (in Earth science and astronomy) The cold regions of the planet that exist farthest from the equator; the upper and lower ends of the virtual axis around which a celestial object rotates.
solar system: The eight major planets and their moons in orbit around our sun, together with smaller bodies in the form of dwarf planets, asteroids, meteoroids and comets.
star: The basic building block from which galaxies are made. Stars develop when gravity compacts clouds of gas. When they become hot enough, stars will emit light and sometimes other forms of electromagnetic radiation. The sun is our closest star.
sun: The star at the center of Earth’s solar system. It is about 27,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Also a term for any sunlike star.
technology: The application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, especially in industry — or the devices, processes and systems that result from those efforts.
telescope: Usually a light-collecting instrument that makes distant objects appear nearer through the use of lenses or a combination of curved mirrors and lenses. Some, however, collect radio emissions (energy from a different portion of the electromagnetic spectrum) through a network of antennas.
unique: Something that is unlike anything else; the only one of its kind.
volcano: A place on Earth’s crust that opens, allowing magma and gases to spew out from underground reservoirs of molten material.
"dazzling" - Google News
February 21, 2020 at 06:45PM
https://ift.tt/2SK4Sfk
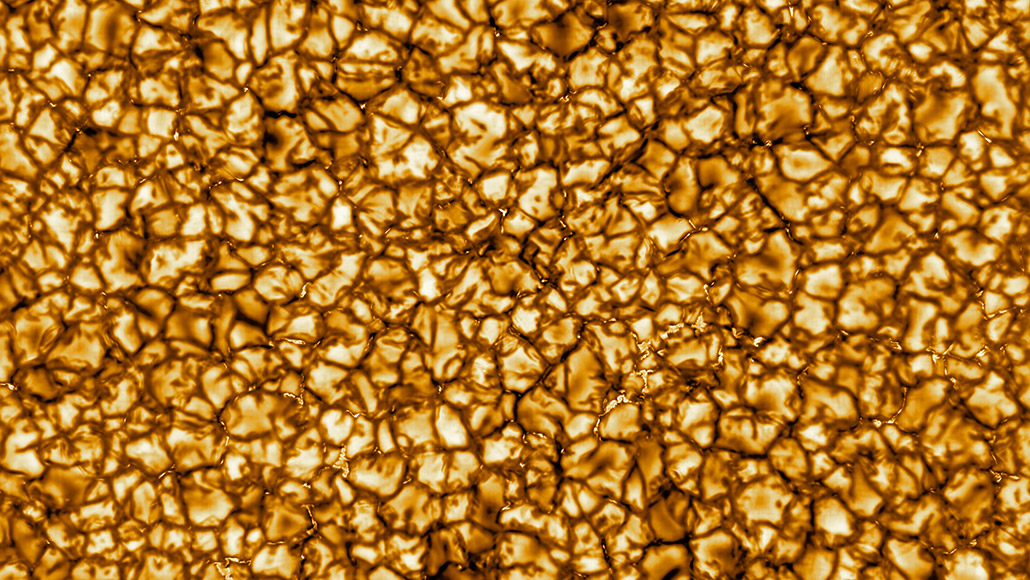
See the sun in dazzling detail - Science News for Students
"dazzling" - Google News
https://ift.tt/2SitLND
Shoes Man Tutorial
Pos News Update
Meme Update
Korean Entertainment News
Japan News Update
Bagikan Berita Ini















0 Response to "See the sun in dazzling detail - Science News for Students"
Post a Comment